Your business may not be ranking in the top positions of search results because of common SEO mistakes. SEO is probably the hardest channel to master because it has migrated from a silo activity palmed off to a nerd that gets fed Coke in a dark room, to a profession that involves teams across development, design, content, and management that must work together.
I see small businesses make the most mistakes given their team-size limits what they can do, yet large businesses still screw up the fundamentals. Google itself admits to making SEO mistakes! Gary Illyes from Google describes how staff messed up hreflang tags, which set the language and region of a webpage, in Google’s own help center. “Someone was trying to target Los Angeles and thought using ‘LA’ as a country code would be great. It actually means ‘Laos’.”
Everyone makes mistakes—what matters is if you learn from them. Whether you make these SEO pitfalls from miss-information or lack of education, it’s time to fix them with this complete guide to educate you on what you should be doing.
The effort to get your SEO right is worth it. SEO has many benefits such as increasing brand visibility, organic traffic, and sales from search results. Once your website gets on the first page of Google, every jump in position sees your click-through rate from search listings increase up to 32% in the first position. You will be more prepared for the future since the SEO industry is predicted to grow at a rate of 14.4%, reaching US$1.6 billion by 2027.
I’ve kept the guide up-to-date with the most frequent hiccups made by marketers in SEO. This list has come from my experience training several people who have gone from knowing nothing about SEO to being world-class, auditing the SEO of Shopify stores every month, and helping people generally in SEO every week.
Whether you get an expert to tackle your website optimization or choose to do it yourself, here are the 11 common SEO mistakes to avoid and how to fix them.

1. Using Rankings as the Measure of SEO Success
Rankings as a metric by itself does nothing. If you rank high, does that mean you get traffic? If you get traffic, does that mean you get sales?
How to Fix It
You should instead use four metrics that are Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) of good SEO:
- Organic traffic – Rankings are useful once they start bringing in traffic. You can rank #1 for many terms yet receive no visitors. Compare that to ranking #10 for a popular term and getting a sale from it everyday because your prospective customers heavily use the search query.
- Organic leads – Each keyword consists of a market. Track which keywords get you leads to optimize your website around those keywords.
- Organic revenue – If you have an ecommerce store, you have no excuse to not track revenue from organic search. It’s simple to setup through Google Analytics. See my Shopify and Google Analytics guide to get your Shopify store setup to track revenue.
- Multi-channel revenue contribution – If someone discovers your company through organic search, signs up to your newsletter, then later buys from you, track the organic contribution to the sale rather than attributing it purely to the newsletter. Organic search in this case should be acknowledged as a contributor to the bottom line. Google Analytics 4 does a good job at showing you multi-channel contribution.
With these four KPIs of SEO, you’re ready to do SEO well and avoid other common mistakes.
2. A Slow Website Speed
A slow website speed can make you lose traffic gained from search results. A recent survey carried out on online shoppers found that every fourth person would click off a page and abandon their purchase if a website takes more than 4-6 seconds to load, thus thwarting your SEO efforts.
53% of the customers said the acceptable time for a business page to load is 3 seconds at most. Therefore, if your website can load this fast, you can keep visitors longer on your page. Additionally, 21% of them reported that dealing with a website that loads slowly leaves them frustrated. While the survey is not qualitative user data, the impatience of users aligns with older classic statistics on speed.
Google has disclosed that its algorithm takes into account a website’s speed when deciding where to rank it on search results. A slow website speed can negatively affect your ranking.
If you’d like to review your website speed, use GTmetrix and Google’s lighthouse through web.dev.
How To Fix It
There are various steps you can take to improve your website’s speed and they include:
- Resize images. Unoptimized images slow down a website because they take more bandwidth to load. You can manually resize images in picture editing tools or use apps that automatically compress images uploaded on your website. Below, the image on the left with no compression is 30 times larger than the optimized version, and is likely to take 30 times longer to fully load. The large image isn’t used in a one thousand pixel height format to warrant its excessive dimensions.

- Choose image formats that are smaller in size. Use tools like Photoshop to test exporting the image in different formats. You will see size differences. An excellent example is JPEG, which takes up less memory compared to GIF or PNG for most images.
- Fix redirects. When visitors are redirected to another section or page of your website, that page takes longer to load since it waits for the server to respond to the redirect HTTP request. Get rid of as many redirects as you can by linking straight to the source. Screaming Frog is the best way to identify all internal links that redirect. Some redirects are necessary like shortened URL handles for offline promotions. Do away with ones you can avoid to increase your website speed.
- Compress JavaScript and CSS. Minimize the files to eliminate whitespace, use shorter names for variables, and prevent code-waste with efficient practices.
- Delay the loading of not critical scripts. If JavaScript is inserted inside the “head” tag, it may have to load before anything is seen in the browser. There are ways around this. Should a script be unnecessary for the loading of content above the fold, it may be non-critical and can be loaded before the closing “body” tag.
- Limit the number of apps you have. Not all apps affect Shopify speed. When it comes to increasing your website speed, less is generally more. Check your apps to remove any that are unused. If you discover apps that perform multiple functions, it’s best to use these instead of those that perform single functions since scripts may overlap. Eliminate apps to get the added benefit of saving money from unnecessary expenses.

3. Not Optimizing For The Right Keywords
The SEO mistake of not optimizing for the right keyword can happen when you target broad or generic keywords. Broad keywords have a lot of competition and so a small business has no chance of ranking for them. Sally in Longreach, Australia, who knits jumpers for women is not going to rank number one for “women’s jumpers”.
Another way you may also be messing up your SEO is by optimizing the wrong keywords. These can be words sprinkled in your articles or pages that are unrelated to what you do or the topic of the blog. Even worse, you can end up confusing visitors.
When you use the right keywords, you attract your target audience and make them stay long enough on your website to make a sale, visit another section of your website, or sign up to your newsletter.
How To Fix It
- Pay attention to search engine results pages (SERPs). Before you come up with content for your website, search that problem or question to see what information your potential competitors provide. The aim is to provide better or more information than them so anyone who visits your page leaves satisfied.
- Check the format that the pages ranking high are using to answer user intent. Is the information provided in the form of blog posts, product reviews, or how-to guides? Do they have a lot of images or videos? Since this is what is working, emulate the same format or adjust your keywords. You have no chance at ranking an article for “buy glass windows” if the top 5 search results are collection pages of stores selling glass windows.
- Understand your potential customer’s language. How would a potential customer type that in Google? Let’s say you supply “electronic nicotine delivery systems”, is that how your customer would search online? Unlikely. How about “electronic cig” or “electronic cigarette”? Definitely, yet what do you go for? Compare the terms in Google Trends. “Cig” is hardly used so you’d want to use the higher volume variant in your optimizations such as “Electronic Cigarettes Australia”. Listen to the words used by people who want what you have to sell.

- Conduct thorough keyword research to know realistically which terms you are likely to rank for. The “Keywords Explorer” in ahrefs is an amazing tool you can use to estimate the competitiveness of a keyword. The “Keyword Difficulty” rating gives an estimation of how hard it is to rank in the top 10 organic search results for a keyword on a 100-point scale.

- Use long-tail keywords. These keywords are longer, less competitive, and focus on specific qualities. Long-tail keywords get less web traffic and higher conversion rates increase since people find what they want. Not everyone searching a broad keyword has the same intent that lines up with the specific version. Too much search-engine optimization is done around a keyword before asking yourself if the content of a page genuinely serves people who search the keyword. In the example of Sally with her jumpers, she has a chance of ranking for “women’s jumpers longreach” or “women’s knitted jumpers australia” without having to get many backlinks and spending a lot of time improving her store’s SEO.
4. Unoptimized Title Tags And Meta Descriptions
Title tags are the second biggest influence of on-page SEO following good content. Meta descriptions are less important today than they were years ago, but mostly influence someone’s desire to click-through.
Google checks the keywords in your title to majorly determine what the page’s content is about. These keywords hold more water compared to the ones you put in your blog content or product descriptions. You define a title tag with a line of HTML in the <head> tag of a page:
<title>This Is A Page Title</title>
It commonly displays in the browser tab of a page and as blue text in Google search results.
Meta descriptions in search results are colored black and inform people what to expect on the page. So, if you leave it blank or write a poor one, it doesn’t fulfil this function. You can define a page’s meta description with the following code in the <head> tag of a page:
<meta name="description" content="Here is a description of a page. The text here will show in Google." />
Here’s a screenshot of a Google search result showing 3 titles in blue text and 3 meta descriptions in black text.

Google is likely to modify titles and meta descriptions that are not unique, fail to summarize the page, and provide no specific information to people searching. The SEO mistake of unoptimized title tags and meta descriptions forces Google to come up with a summary of your page, which isn’t ideal because you miss the chance to craft sentences that get a higher click-through rate.
How to Fix It
The good news is this common SEO mistake is one of the easier to correct. Best practices for titles and meta descriptions include:
- Relevancy. Write descriptive, keyword-rich titles readable by people. Make the description relevant to the page as well.
- Make titles and meta description unique to each page. It’s easier to be unique when you keep relevancy top-of-mind.
- Have your major keywords at the front of the title tag.
- Give titles a length between 50 and 60 characters and meta descriptions a length between 145 and 160 characters.
- Add potent benefits in the title to entice people to visit, though generally, look to include them in the description because of character limits. If you have any selling propositions like free delivery or a guarantee, include them in the description to attract visitors.
5. Unengaging Information
“Content is King” because not providing high-quality information is the fastest way to lose visitors.
Gone are the days when websites could publish poorly written blogs for the sake of having something on their website. It’s not enough to put keywords in your content since the information, and the way the keywords are used, need to make sense to the reader. If your competitors provide the helpful information or guidance your customers need and you don’t, then you can guess where people are spending their money.
Of course you want people to buy your products or services rather than only engage in your content. The belief that you should only get bottom of funnel people ready to buy, however, constrains your growth to the hundreds of multiples of people higher in the funnel not yet to ready to buy. When you satisfy people, you increase your chances of ranking higher on search results. When users spend time on your website, they may come back or even refer their friends.
How To Fix It
- Visit your website now then read over it pretending you’re a visitor. Ask, “Am I learning something? Do I get the information I need? Have I never read information like this on other websites?” If you said yes, yes, and yes, well done. If you said no once, rework the website. The common ecommerce SEO mistake uses the manufacturer’s description, which offers readers no unique information.
- Read over the top 4 Google search results of a query you want to rank for. These reveal where content gaps exist and opportunities for you to cover topics not already talked about, or to go into more depth about a topic, thereby creating a more useful article for the reader. You must give Google a reason to rank the content higher than what’s currently in the top 4 positions.
- Have fresh content on your website. Google and people appreciate this because the most recent information is usually more accurate. You can achieve fresh content by reviewing all content on a yearly basis and implementing a content strategy. You don’t need a blog. Good content can come from Shopify collections, product pages, and YouTube videos. If you want to blog for SEO, contrary to what a lot of SEO experts tell you, you don’t need to be writing every week in an effort to please Google. A high-quality monthly guide is better than weekly trash.
- Use supplementary materials to increase value. Supplementary materials help people get more out of the topic at hand like a how-to guide that has a text tutorial and a video for a practical question. Another complementary resource is infographics that can get backlinks. Our hreflang guide for Shopify includes a Shopify app plus a Google Sheet and tutorial to help merchants get their hreflang tags right. There are experts to follow on Instagram who specialize in data visualizations. Supplementary content ideas include:
- The “concept visual”
- Native video
- Ultimate guides
- Infographic guest posts
- Data visualizations
- Videos
- Flowcharts
- Explainer infographics
- Screenshots
- SlideShare slide decks
- Interactive content
- Visual collection
- Co-branded infographics
- Cartoons and comic strips
- Maps
- Blog post banners
- Templates like Google Sheets
- Provide key takeaways for the reader at the end of the article so they do not have to return to Google to search for more answers. Google tracks when users return to search results to find more information as it shows the user is not fully satisfied. You want the reader to click away fulfilled from their search.
6. Unfriendly URLs
An unfriendly URL is hard to understand, ugly, or big. Here are examples of unfriendly URLs:
http://www.example.com/index.php?option=com_content=2©=1taskview&id+312<emid=43http://www.example.com/a/b/c/d/e/f/article1http://www.example.com/title-of-an-article-that-goes-on-forever-like-a-bad-movie-that-never-ends
Unfriendly URLs in Shopify tend to occur on filters of collections where parameters get appended to URLs that make no sense.
How to Fix It
Avoid unfriendly URLs with these simple rules for friendly URLs:
- Keep them short.
- Make them descriptive of the page.
- Avoid deep URL structures. These include a lot of forward slashes.
- Avoid query strings. These are variables after the question mark character (“?”) and may contain the ampersand symbol (“&”).
- Use hyphens (a good webmaster practice) rather than underscores.
- Logical and structured. For example, articles are in an article folder and products are in their product category. Shopify automatically does this for you.
7. Faulty Response Codes
Every webpage gives a response code. The most valid response code is a 200 as it means the request succeeded.
The 404 response code occurs when a page doesn’t exist, which creates a bad user experience. A 404 can be valid, but it is an SEO mistake when the page exists elsewhere or the link to a 404 existed somewhere on the website.
Redirects give various response codes as they guide a visitor to a page whenever you modify or remove content. Faulty redirects take users to the wrong page or generate errors.
Customers can be frustrated dealing with non-200 response codes and can leave your website altogether, therefore, increasing your bounce rate and reducing the amount spent on it. The end result is ranking lower on search results.
How to Fix It
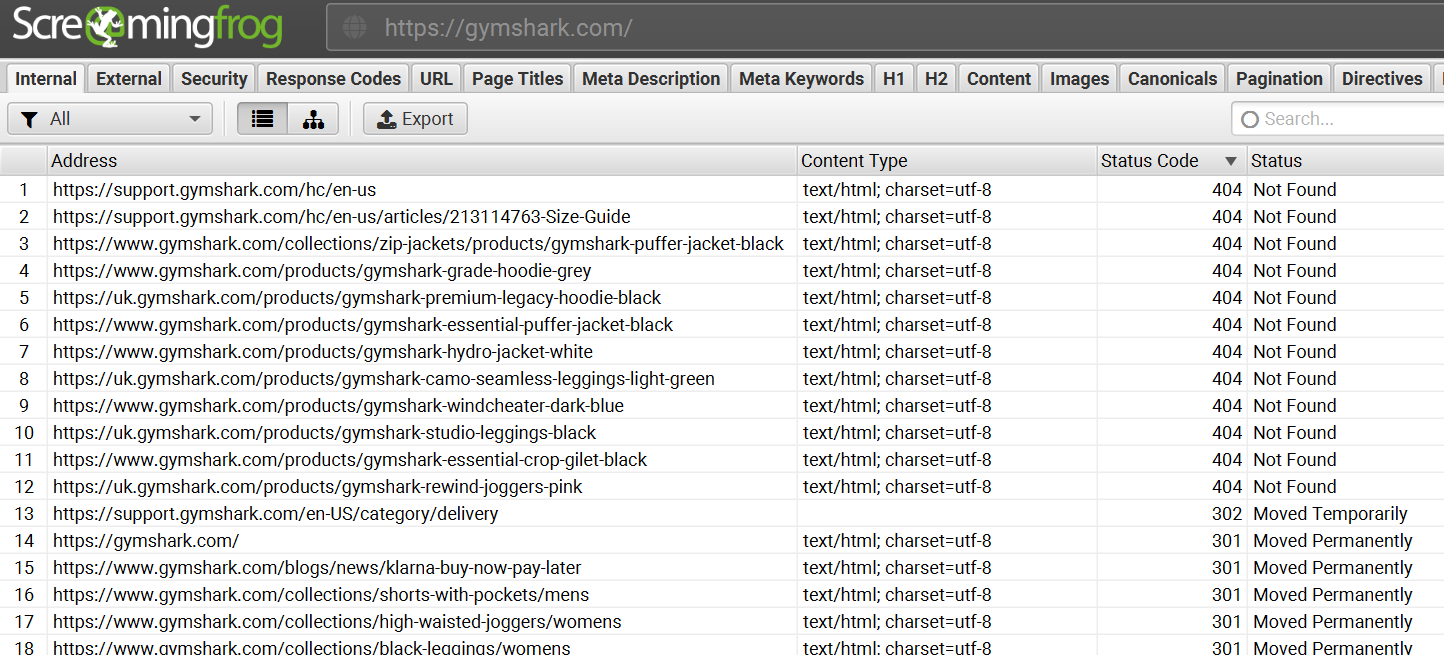
- Google Search Console and Screaming Frog are the best tools to see all the response codes on a website. Below you can see a screenshot of a Screaming Frog crawl of Gym Shark’s website that contains many faulty response codes.
- Avoid changing your URLs where possible unless there’s a strategic reason or they’re being optimized.
- For broken external links, remove or replace them with working links. If people click on the links to access the website you’ve recommended and they get an error, it decreases trust.
- For faulty internal links, check if there’s a typo in the URL that is causing the error and fix it. This is sometimes the case with 404 errors.
- Google recommends using 301 redirects if you have permanently moved content to another page. Any native redirect in Shopify is a 301. Additionally, Google says you should have that redirect active for 1 year to give it time to register that change and apply it to search results. If the page move is temporary, a 302 redirect is more appropriate.
8. A Non-Mobile Friendly Website
How does every page on your website look on a mobile phone or tablet device?
59.3% of people access websites through their mobile phones. A non-mobile friendly website can cost you traffic and sales when people click off your website in preference to others that are easier to navigate. When visitors continue to leave your website, Google knows it doesn’t serve people and is less likely to place it at the top of search results.
A mobile-friendly website is even more important now. Google created a mobile-first indexing crawler in September 2020. Its algorithm gets snippets for search results from the mobile version of a page and mainly uses a websites’ mobile version to determine rankings.

How To Fix It
- Use device mode in Chrome to easily check how your website looks on all the major devices, from iPhones and Android tablets, to iPads and Nest Hubs.
- Conduct a Google Mobile-Friendly Test for ideas to make a page more mobile-friendly.
- Have a website design specifically made for mobile users using responsive design. When someone accesses your website from their phone, it adapts to the mobile layout and screen size. A responsive design is easier to manage as you update only one website.
- Get rid of large chunks of text on your website, especially the home page. It’s harder to format and read chunks of texts clamped together on a mobile phone compared to a computer. The goal is to make it easier for your customers to read the information they need.
- Use images that take up as little space as possible to maintain a good loading speed.
- Place buttons in the right place. Think about how you hold your phone and use your thumb to click a link or button.
9. Pages Not Indexing
The most common way a search engine discovers a web page is through crawling, where the search engine’s bot follows links on the web to find new pages and add them to their index. When your pages are not indexed, people cannot find them on search results. It is impossible to rank a page on Google unless the page is first indexed.
The Googlebot every second is searching the internet for new or updated pages. This is called “crawling”. After Google crawls your page, it analyzes what your website is all about, which is referred to as “indexing”. The “Page indexing” report in Google Search Console shows what content on a website is indexed and what is not indexed.

If you have created a page that has high-quality content, has an optimized title tag and meta description, is linked internally on the website, and satisfies user intent, you’ve given Google a great chance at crawling then indexing the page. From here, Google can show your page on search results.
You may be asking yourself how a page not being indexed is an SEO mistake that’s your fault. Although it is up to Google to index your page, some factors hinder this process and these are what you should fix.
How To Fix It
- If you just created a website or page, give Google some time to discover it. A new website can take up to 3 weeks to discover.
- Get rid of 404 errors and use 301 redirects instead. If some of your pages were ranking well in search and then you restructured your site or changed domains, check for these errors because they might have occurred during the move.
- Use high-quality content. If you’ve published duplicate content, Google may only index the original content.
- Solve the problem of manual actions on your website. If Google determines that you’ve gone against their quality guidelines, they can declare a manual action against your website. The result is your website can rank low or be taken off search results.
- Update your sitemap. An outdated sitemap makes it hard for Google to access your URLs, thus making it hard to accurately rank you in search.
- When you create a new page, see if it is linked to from another page on the website. If a page has no internal links, it is considered an orphan page and may not be found by Google. The search engine discovers most pages by following links. Internal links help indexation as well as rankings.
10. Hiring a Bad SEO company
There is a lot of bad SEO out there due to the ever-changing field and lack of regulation. If you pay for links, outsource to a cheap overseas company, hire an untrained intern, or try to save a buck, you often pay for it with no progress in rankings or even worse, a Google penalty.
How to Fix It
- Ask these 7 questions to your SEO company to figure out if they should do your SEO.
- Play an active role in monitoring results by tracking SEO KPIs mentioned at the start of this guide.
11. Not Understanding How SEO Works With Other Channels
Another common SEO mistake marketers and business owners make is failing to understand how SEO integrates with other channels or parts of a business. When you don’t make SEO part of your digital marketing strategy, you miss optimizing a channel that is already happening whether you choose to be intentional about it or not.
Let’s look at how SEO can work with other channels.
- Social media: Engagement on social media often leads to people searching your brand in Google. A Facebook ad may not lead to a sale from the ad, yet it can from a Google search. You can build your presence on Facebook, Instagram, and to a lesser extent TikTok, by sharing blog posts. Videos on social media can be crafted to tease someone into searching Google or visiting a page made for SEO.
- Paid search: Google Ads lets you see high-volume searches and good converting keywords that you can translate to your SEO keyword strategy. On the flip side, you can discover what keywords have poor commercial value before spending months chasing them or wasting thousands of dollars on poorly targeted content. Query data is obscured with Performance Max campaigns so be conscious of this when making Google Ads optimizations.
- Referral links: You can find a way to share valuable information at an event or with people in your industry or community. By doing this, you’re building an audience of people who trust you. Perhaps you left a video testimonial for your accountant. An SEO expert will want to grab backlinks from these creative sources to help your SEO.
Aside from influencing and being influenced by other channels, SEO affects all aspects of a business.
- Developers need to be guided by an SEO expert to improve page speed, shape the architecture of a website, craft a faceted filtering system that is SEO-friendly, and more.
- Designers need to be guided by an SEO expert to create graphics that load fast and support existing content to improve its value.
- Writers need to be guided by an SEO expert to produce content that’s backed in research, relevant, and better than anything previously published.
How To Fix It
You can correct this SEO mistake by:
- Reminding yourself of the truths shared above.
- Consider data from all your digital marketing channels when creating your SEO strategy. Refer to Google Analytics 4 to see how the organic search channel moves with other channels. TripleWhale is an incredible tool for Shopify businesses to understand how all marketing channels work together so they can profitably grow.
Fix These Common SEO Mistakes To Improve Your Ranking
Did you spot some common SEO mistakes you’ve been making?
If the answer is yes, you don’t need to beat yourself up about it. Even SEO experts slip up sometimes. The most important thing is you know the steps to fix these errors.
Now get out there and make your page rank better on search results.
If you’re looking to optimize your Shopify store for search engines, check out our SEO service.
To master Shopify SEO, I’ve got another great video for you. It took me 15 years to fix these 5 huge mistakes that destroy organic traffic of ecommerce stores and other websites.
When my brother Matt was looking for work, he knew nothing about SEO so I wanted to see how fast he could become world-class if he avoided these 5 huge mistakes. So I hired him at Digital Darts. In 6 months, he is growing stores by himself, which took me 15 years. Watch how:
FAQ on SEO Challenges
What negatively affects SEO?
- Slow page speed
- Keyword stuffing
- Not using title and meta tags
- Unengaging information
- Unfriendly URLs
- Faulty response codes
- A non-mobile friendly website
- A poor website structure
- Not having a secure website
- Hiring a bad SEO company
Why does SEO fail?
SEO can fail if the business does not have a clear strategy, proper technical SEO, quality backlinks, good content, and good user experience.
What is the biggest challenge of SEO?
The biggest challenges in SEO is having the resources to implement technical improvements, a content plan, and a backlink strategy.
Liked this article? Get more free Shopify guides:
Enter your primary e-mail address to receive notifications when there are new educating Shopify tutorials and free practical tips to increase sales. You'll also immediately download a 30+ page deck "4 Rules of Store Growth: To Sell More on Shopify, Escape Work You Hate, Boost Profit, and Have a Business You're Proud Of".



4 Comments. Leave new
Thanks for sharing common SEO mistakes
Hey Joshua
Thanks for the great tips! I’m new to online marketing, and this is really helpful! Since getting started, I’ve been bombarded by “spin writers” and such to create a TON of content quickly, but you seem to say that these search engines have become sophisticated enough to determine when your content is crap. Am I understanding that right?
You make some great points 🙂 I see so many businesses who have a beautiful website, but don’t even optimise something as simple as metadata. And yes, “bad keywords” is a great point. Good keywords include those that actually have traffic that is actually being searched by those who matter!
Great post overall! I can see this being very handy for a lot of business owners.
Fantastic guide! “Dummies Guide to Common SEO Mistakes” breaks down complex concepts into easy-to-understand tips. The section on avoiding keyword stuffing and focusing on quality content is especially helpful. This is a must-read for anyone looking to improve their SEO strategy. Thanks for the practical advice!